Want to Reduce Political Extremism? Ask How Instead of Why
1. What They Did – Intervention Summary:
All participants began by rating their positions on six political policies. They then self-assessed their understanding of these policies using a series of 7-point rating scales. Next, some participants were asked to explain in detail how one of the policies works, while other participants were asked only to list the reasons they had for holding their position on that policy. Finally, all participants were asked to rerate both their understanding of the policy and their position on the policy. Participants repeated this process for one additional issue.
2. What They Found – Results:
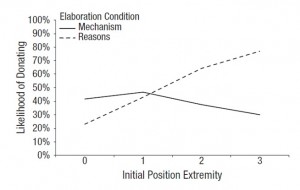
Those who had had to explain how the political policies worked became less confident in their understanding of those policies than did those who had been asked to enumerate reasons for their positions. Further, participants reported more moderate attitudes towards the issues after giving mechanistic explanations, whereas enumerating reasons led to no such change in position extremity.
3. Who Was Studied – Sample:
MTurk users- 50% male, 50% female
4. Study Name:
Fernbach et al., 2013, Study 2
5. Citation:
Fernbach, P. M., Rogers, T., Fox, C. R., & Sloman, S. A. (2013). Political extremism is supported by an illusion of understanding. Psychological Science, XX(X), 1-8. doi:10.1177/0956797612464058
6. Link:
http://scholar.harvard.edu/files/todd_rogers/files/political_extremism.pdf
7. Intervention categories:
generating mechanistic explanations, mTurk
8. Sample size:
112
9. Central Reported Statistic:
“the decrement in understanding after enumerating reasons was smaller than the decrement following mechanistic explanation, as reflected by a significant interaction between judgment timing and condition, F(1, 110) = 6.64, p < .01, ηp2 = .057. With regard to extremity of positions, there was no change after enumerating reasons, F(1, 64) < 1, n.s. Moreover, as predicted, the change in position in the reasons conditions was smaller than in the mechanism conditions, as reflected by a significant interaction between judgment timing and condition on extremity scores, F(1, 110) = 3.90, p < .05, ηp2 = .034.”